Bodybuilder gynecomastia is a condition that affects many in the fitness community.
Whether you’re a seasoned competitor or a gym newbie, understanding bodybuilder gynecomastia is crucial for maintaining optimal health and achieving aesthetic goals. Let’s uncover what causes this condition in athletes, how to identify its symptoms, and most importantly, what treatment options are available for those affected.
Gynecomastia: Definition, Causes and Prevalence in Bodybuilders
Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males and glandular tissue growth.
But why are bodybuilders more susceptible? The answer lies in hormones. Bodybuilders often push their bodies to extremes, which can disrupt the natural hormonal equilibrium. When estrogen levels rise relative to testosterone, breast tissue can begin to develop.
This hormonal imbalance can be triggered by intense training, certain supplements, and, yes, steroid use. Gynecomastia on bodybuilders is more common than you might think, especially with the introduction of anabolic steroids in male athletes.
Understanding the causes of gynecomastia in bodybuilding is crucial for prevention and treatment, as the condition can be closely linked to training practices and supplement use. While genetic predisposition may play a role, many cases in bodybuilders are linked to external factors — things we can potentially control. These include diet, training intensity, supplement use, and of course, the use of performance-enhancing drugs.
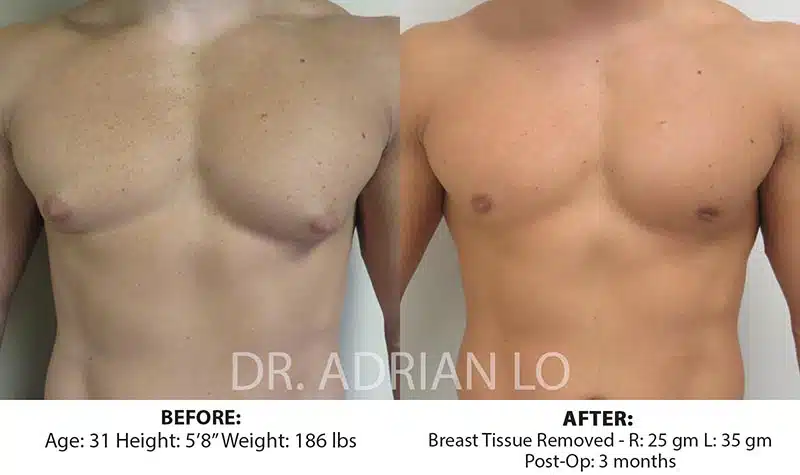
Looking into gynecomastia surgery to get back to your confident self? Schedule a consultation with Dr. Adrian Lo to get one step closer to your journey!
Common Steroids Linked to Gynecomastia

Let’s discuss steroid-induced gynecomastia, a common side effect of anabolic steroid use in bodybuilding. It’s no secret that some bodybuilders turn to anabolic steroids to enhance their performance and physique, but this practice can lead to gynecomastia in athletes across various sports. While we’re not here to judge, it’s crucial to understand the risks. Steroid use is one of the most common causes resulting in individuals bodybuilding with gynecomastia.
Why do bodybuilders take this risk? The allure of rapid muscle growth and enhanced performance can be hard to resist in a sport where size and strength are everything. But it’s a double-edged sword. The same compounds that build muscle can also upset your body’s hormonal balance, potentially leading to gynecomastia.
Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids (AAS)
These synthetic substances mimic the effects of testosterone, promoting muscle growth and male characteristics. However, they can also convert to estrogen in the body through a process called aromatization.
Common Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids (AAS) associated with gynecomastia include testosterone, nandrolone, and methandrostenolone. These steroids can dramatically increase estrogen levels, leading to breast tissue growth.
The risks extend beyond gynecomastia. AAS use can lead to liver damage, cardiovascular issues, and psychological effects. It’s a high price to pay for gains, and it’s why many in the bodybuilding community are advocating for natural alternatives.
Corticosteroids
While less commonly associated with gynecomastia in bodybuilders, corticosteroids are worth mentioning. These are different from anabolic steroids and are often used to treat inflammation or autoimmune conditions. However, long-term use of high doses can potentially contribute to gynecomastia.
Corticosteroids work differently from AAS but can still disrupt hormonal balance. They’re less likely to be abused in bodybuilding circles, but it’s important to be aware of their potential effects, especially if you’re using them for medical reasons alongside your training regimen.
Mechanism of Action
Understanding how steroids lead to gynecomastia is key to prevention. It all comes down to hormonal balance. When you introduce exogenous (external) hormones into your body, you’re tinkering with a finely tuned system.
Many anabolic steroids can be converted to estrogen through an enzyme called aromatase. As estrogen levels rise, they stimulate the growth of breast tissue. It’s the same process that occurs naturally in puberty, but in this case, it is caused from the use of steroids.
The degree of aromatization varies between different steroids and individuals. Some bodybuilders attempt to counter this effect with aromatase inhibitors, but this approach comes with its own risks and should only be done under medical supervision.
Symptoms of Bodybuilder Gynecomastia

For bodybuilders, who are typically hyper-aware of their physiques, even subtle changes can be noticeable. However, it’s important to distinguish between true gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia, which is simply fat accumulation in the chest area.
Breast Tissue Enlargement
The most obvious sign of gynecomastia is an increase in breast tissue. You might notice a firm or rubbery mass underneath the nipple area. In bodybuilders, this can be particularly distressing as it disrupts the desired chest contours.
The enlargement is often symmetrical, affecting both breasts equally. However, in some cases, it may be more pronounced on one side. The tissue may feel firm and disk-like, distinct from the softer feel of fat tissue.
Tenderness or Pain
Gynecomastia isn’t always just a visual issue. Many men experience tenderness or pain in the affected area. This can range from a mild discomfort to a more pronounced pain, especially when the area is touched or pressed.
For bodybuilders, this can be particularly problematic. Chest exercises might become uncomfortable or even painful. You might find yourself avoiding certain movements or unable to train with the same intensity.
Nipple Changes
Gynecomastia can also cause changes to the nipples and areolas. You might notice that your nipples become more prominent or puffy. The areolas (the darker area surrounding the nipple) may also enlarge or change shape.
These changes can be subtle at first but may become more pronounced over time. For bodybuilders, who often have low body fat percentages, even small changes in this area can be quite noticeable.
Keep an eye out for any asymmetry or unusual changes in nipple appearance. While some variation is normal, significant changes could be a sign of developing gynecomastia.
Texture Changes
As gynecomastia develops, you might notice changes in the texture of your chest tissue. The affected area may feel firmer or have a different consistency compared to the surrounding tissue.
In the early stages, you might feel a small, firm lump beneath the nipple. As the condition progresses, this can expand to a larger area of firm tissue. The skin over the affected area might also feel different — perhaps tighter or more sensitive.
Non-Surgical Treatments
If you’ve identified signs of gynecomastia, don’t despair. There are several non-surgical treatment options available, especially if caught early.
Medication and Hormone Therapy
Medication can be an effective first line of defense against gynecomastia, especially when hormonal imbalances are the root cause. Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen or raloxifene are commonly prescribed. These drugs work by blocking the effects of estrogen in breast tissue.
Aromatase inhibitors, which prevent the conversion of testosterone to estrogen, may also be used. However, these should be used cautiously and only under medical supervision, as they can have significant side effects.
In some cases, hormone replacement therapy might be recommended to restore proper hormonal balance. This is particularly relevant for bodybuilders who have disrupted their natural hormone production through steroid use.
Lifestyle Modifications
Sometimes, simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference. If your gynecomastia is linked to diet or training practices, adjusting these factors can help.
Some studies suggest that certain foods, like cruciferous vegetables, may help balance estrogen levels. Your training regimen might also need tweaking. While it might seem counterintuitive, overtraining can actually contribute to hormonal imbalances. Ensure you’re getting adequate rest and recovery time between workouts.
Compression Garments
For some bodybuilders, compression garments can provide a temporary solution while addressing the underlying cause of gynecomastia. These specially designed shirts or vests apply pressure to the chest area, helping to flatten and conceal enlarged breast tissue.
Compression garments come in various styles, from tank tops to full shirts. Some are designed specifically for gynecomastia, with extra compression in the chest area. While they don’t treat the condition, they can help you feel more confident and comfortable, especially during workouts or competitions.
Surgical Treatments
When non-surgical treatments aren’t effective, or if gynecomastia is severe or long-standing, male breast reduction for bodybuilders might be the best option to restore a masculine chest contour. Surgical intervention can provide dramatic, immediate results, but it’s important to understand that it is a surgical procedure with minimal risks with a 1-2 week recovery period.
Liposuction
Liposuction is often the first-line surgical treatment for gynecomastia, especially when the enlargement is primarily due to fatty tissue. This procedure involves making small incisions and using a cannula to suction out excess fat.
For bodybuilders, liposuction can be particularly effective because it allows for precise contouring of the chest area. It’s less invasive than other surgical options and typically has a shorter recovery time.
Liposuction alone may not be sufficient if there’s a significant amount of glandular tissue present. In these cases, gynecomastia excision surgery along with liposuction may be recommended for optimal results.
Most bodybuilders have true glandular gynecomastia which will necessitate gland removal by excision.
Excision Surgery
When gynecomastia involves a substantial amount of glandular tissue, excision surgery is often necessary. This procedure involves making an incision around the areola or in the natural creases of the chest to remove the excess glandular tissue. This procedure is called subcutaneous mastectomy.
Excision surgery removes the glandular breast tissue, resulting in a flatter, more masculine chest contour.
Any glandular breast tissue that is removed should be sent to Pathology for analysis. In most cases the removed breast tissue is normal. In rare occurrences, the removed breast tissue may have pre-cancerous or cancerous cells. Sending any excised breast tissue for Pathology gives one the piece of mind that the breast tissue is gynecomastia and not breast cancer.
The incision around the areola usually heals almost invisible, especially when performed by a skilled plastic surgeon .
Nipple Repositioning and Areola Reduction
In some cases of severe gynecomastia, the nipples and areolas may have become stretched or displaced. In these situations, nipple repositioning or areola reduction may be necessary to achieve a natural-looking result.
These procedures are typically performed in conjunction with gynecomastia excision surgery. The nipple-areola complex can be repositioned higher on the chest wall, and the areola can be reduced in size if necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s address some of the most common questions about gynecomastia surgery.
What Can I Expect After Gynecomastia Surgery?
Gynecomastia surgery recovery for bodybuilders requires special consideration, as it’s crucial to balance proper healing with the desire to return to training. Recovery varies depending on the extent of the procedure, but most patients can return to light activities within a week. You will likely experience some swelling and discomfort for the first few days, which can be managed with over the counter medications.
A compression garment will be worn for several weeks to help reduce swelling and support the new chest contours. Upper body workouts may be resumed at 2 weeks,
Will My Gynecomastia Come Back?
If the underlying cause of your gynecomastia is addressed, recurrence is unlikely. However, if you return to habits that triggered the condition initially (like steroid use), it’s possible for gynecomastia to return.
Preventing gynecomastia in bodybuilding involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, appropriate exercise routine, and careful consideration of supplement and steroid use. If you’re a bodybuilder using anabolic steroids, work with your doctor to develop a proper post-cycle therapy (PCT) for gynecomastia prevention, which can help restore hormonal balance and minimize the risk of breast tissue growth.
The breast tissue removed during surgery won’t grow back. However, in rare situations, new gynecomastia can develop if hormonal imbalances persist or recur.
How Do I Know What is the Right Gynecomastia Surgery For Me?
Choosing the right surgical approach depends on various factors, including the severity of your gynecomastia, your body composition, and your aesthetic goals. A consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon is crucial to determine the best approach for your individual case.
Before your consultation, gather information about your medical history, including any supplements or medications you’re taking. Be prepared to discuss your fitness routine and any previous treatments you’ve tried for gynecomastia.
If you’re curious about gynecomastia surgery, schedule a consultation with our New Jersey and Philadelphia plastic surgery offices today!
